The Fundamental Difference
The key difference lies in whether the sensor emits its own infrared radiation or just detects existing radiation.
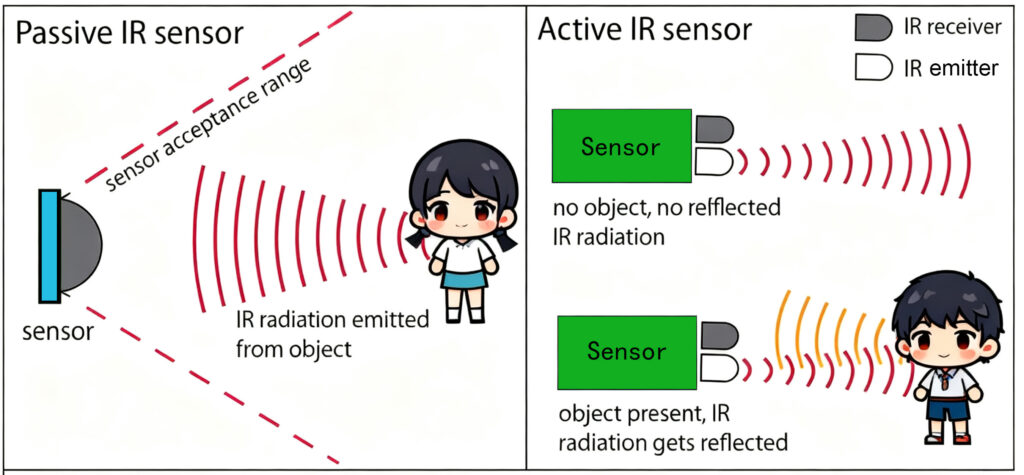
- Active IR Sensors: Have two components: an infrared emitter (like an IR LED) and an infrared detector (like a photodiode). They actively project a beam of IR light into the environment and measure what comes back.
- Passive IR Sensors (PIR): Have only an infrared detector. They do not emit any IR light. Instead, they passively detect the infrared radiation naturally emitted by objects (primarily heat from living beings and objects).
Active Infrared (IR) Sensors
How They Work:
- The sensor’s emitter sends out a beam of infrared light.
- This light travels through the air and either:
- Is reflected back to the detector by an object (proximity sensor).
- Is interrupted by an object breaking the beam (break-beam sensor).
- The detector measures the intensity of the returning light or the change in the received signal.
- The sensor’s circuitry triggers an output based on this measurement.
Applications:
- Proximity Sensors: In smartphones to turn off the screen during a call, in robots to avoid obstacles.
- Object Counting: On assembly lines to count products breaking a beam.
- Distance Measurement: In some autofocus systems and robotics (e.g., IR time-of-flight sensors).
- Safety Systems: Garage door safety sensors that stop the door if the beam is broken.
- Communication: IR data transmission like TV remote controls.
Passive Infrared (PIR) Sensors
How They Work:
- All objects with a temperature above absolute zero emit infrared radiation (heat).
- The PIR sensor’s pyroelectric detector is split into multiple segments (or zones) and is designed to detect changes in infrared radiation levels within its field of view.
- Under normal conditions, the IR radiation from the background (walls, furniture) is stable.
- When a warm object like a human or animal moves through the sensor’s field of view, it first obscures one zone and then another, causing a positive differential change followed by a negative differential change in the detected IR levels.
- This specific change over time is interpreted as motion.
Applications:
- Security Systems: The most common type of motion sensor for burglar alarms.
- Automatic Lighting: Switching lights on in a room when motion is detected.
- Energy Efficiency: Controlling HVAC systems in unoccupied rooms.
- Smart Home Devices: Automatic doors, video doorbells (motion activation).
Fuzhou Rajeyn Electronic Co. normally used active infrared sensor to produce Sensor faucets, automatic concealed cistern, sensor toilet flush, sensor urinal flush, sensor soap dispenser. Welcome to inquiry about our sensor sanitary wares, we are happy to provide detail information.




